1.1.1 Basic terms used in database
1) Data: -A raw fact about anything which does not give any complete meaning.
2) Information: - The processed data which gives some or complete meaning is called information.
3) Database: - An organized collection of data that are shared and used for multiple purposes is called a database. Example: - data of SLC result, Telephone diary, etc.
4) Database Management System (DBMS):
-The software collection which helps to manage the database is called DBMS.
E.g.:- FoxPro, Oracle, Ms-Access, MS SQL, etc.
5) Field: - A field is a piece of information about an element; the element may be a person, student, employee, etc. in figure SN, NAME and PHONE NO are fields.
SN | NAME | PHONE NO |
1 | Pratik Kattel | 984******* |
2 | JANAKI COMPUTER | 021-555477 |
6) Record: - A collection of related fields is called a record. A single row containing one data is a record.
1 | Netra Koirala | 9816347464 |
7) Domain: -A domain is a set of values from which the actual values appear in a given relation, for attribute customer name, the domain is the set of all customer names.
Customer
Customer_name | Account no | Balance |
Raju | A-001 | 4,44,623 |
Sita | A-002 | 10,23,245 |
Shankar | A-007 | 35,25,006 |
8) Tuple: -The row of relation (table) is called a tuple. In this relation below, there are 3 tuples.
Customer
Customer_name | Account no | Balance |
Raju | A-001 | 4,44,623 |
Sita | A-002 | 10,23,245 |
Shankar | A-007 | 35,25,006 |
1.1.2 Objectives or Importance of DBMS: - The following are the objectives of DBMS.
a) To provide huge storage or space for relevant data.
b) To allow easy access to the data for the user.
c) To provide a quick response to the user requests for any information or data.
d) To allow updating with the latest modification in the database.
e) To remove duplicate data.
f) To allow many users to the database at one time.
g) To allow the growth of the database system.
h) To provide maximum protection to data from any physical damage and unauthorized access.
1.1.3 Database Model: -
A database model is the method of organizing data and represents the logical relationship among data elements in the database. The most popular database models are:
1. Relational Model: -
The relational model was formally introduced by Dr. E.F. Codd in 1990. The relational model represents data in the form of two-dimensional tables called relation, which is made of columns and rows. Each column represents a field, also called an attribute, and each row represents a record, also called a Tuple. The domain is a pool of data values from which data is entered into the table for database management. A world of real-world data is called a domain.
Example of Relational Data Model: -
The database has 3 tables (relations):
Employee, Department & Project.
EMPLOYEE (E No, E Name, E Add, E Sal, Gen, DNO)
DEPARTMENT
(D No, D Name, D Location)
PROJECT
( P No, P Name, P Location, E No.)
The entity name is shown in UPPERCASE;
The primary key field is underlined;
The attributes are shown in brackets, separated by commas.
EMPLOYEE
E No | E Name | E Add | E Sal | Gen | DNO |
E1 | AAKASH DANGOL | Kathmandu | 1,00,000 | Male | 2 |
E2 | AAKASH SHRESTHA | Kathmandu | 1,00,000 | Male | 3 |
E3 | ALINA BASTAKOTI | Kathmandu | 1,00,000 | Female | 1 |
E4 | ANJU SHRESTHA | Kathmandu | 1,00,000 | Female | 5 |
E5 | ANU SHRESTHA | Kathmandu | 1,00,000 | Female | 4 |
DEPARTMENT
D No | D Name | D Location |
1 | Library | 101 |
2 | Laboratory | 102 |
3 | Account | 103 |
4 | Examination | 104 |
5 | Discipline | 105 |
PROJECT
P No | P Name | P Location | E No |
1 | English book | 101 | E1 |
2 | Com. Networking | 102 | E2 |
3 | Billing System | 103 | E3 |
4 | Grading | 104 | E4 |
5 | Speaking | 105 | E5 |
Note: - E No is the primary key for table Employee and the foreign key for the table project similarly; D No. is the primary key for the table of the Department and the foreign key for the Employee table. The primary key and the foreign key are the fields that relate tables to each other.
Advantages of Relational Model:-
a) The rules are common in each table and easy to link from one table to another.
b) Normalization of the database is possible.
c) Quick database processing is possible.
d) It has very less redundancy (unnecessary data).
e) It enables a computer system to accommodate a variety of file inquiries in an efficient manner.
f) It also helps to add indexes for the table.
Disadvantages of Relational Model:-
a) It is more complex than other models.
b) It is confusing as many rules are being applied and become non-user friendly.
c) The index portion of the file must be created and maintained along with the file records.
d) In some cases the index portion of the file may be larger than the file with the file records.
e) The file index must be searched sequentially before the actual file records are obtained, resulting in a waste of time.
2. Network Model:-
In the network model, data are represented by a collection of records, and relationships among data are represented by links. A link is an association between records. The records are recognized as an arbitrary graph. A network model is still popular on powerful mainframes.
Advantages of Network Model:-
a) This model is more flexible.
b) It reduces redundancy.
c) Searching is faster.
Disadvantages of Network Model:-
a) It is a very complex type of database model.
b) It needs long programs to handle the relationship.
c) Pointers needed in the database model increase the overhead of storage.
3. Hierarchical Model: -
The Hierarchical data model organizes data in a tree structure. There is a hierarchy of parent and child data segments. Data structure implies that a record can have repeating information,
generally in the child data segments. Data is in a series of records, which has a set of field values attached to it. It collects all the instances of a specific record together as a record type. These record types are the equivalent of rows. To create links between these record types, the hierarchical model uses parent-child relationships. In a hierarchical database, the parent-child relationship is one to many. This restricts a child segment to having only one parent segment.
Advantages of Hierarchical Model: -
a) It is the easiest model of the database.
b) A database owner is more secure.
c) Searching is fast and easy if parents are known.
d) Very efficient in handling ‘one to many' relationships.
Disadvantages of Hierarchical Model: -
a) It is old fashioned, outdated database model.
b) Cannot handle ‘many to many’ relationships.
c) It is a non-flexible database.
d) Increases redundancy.
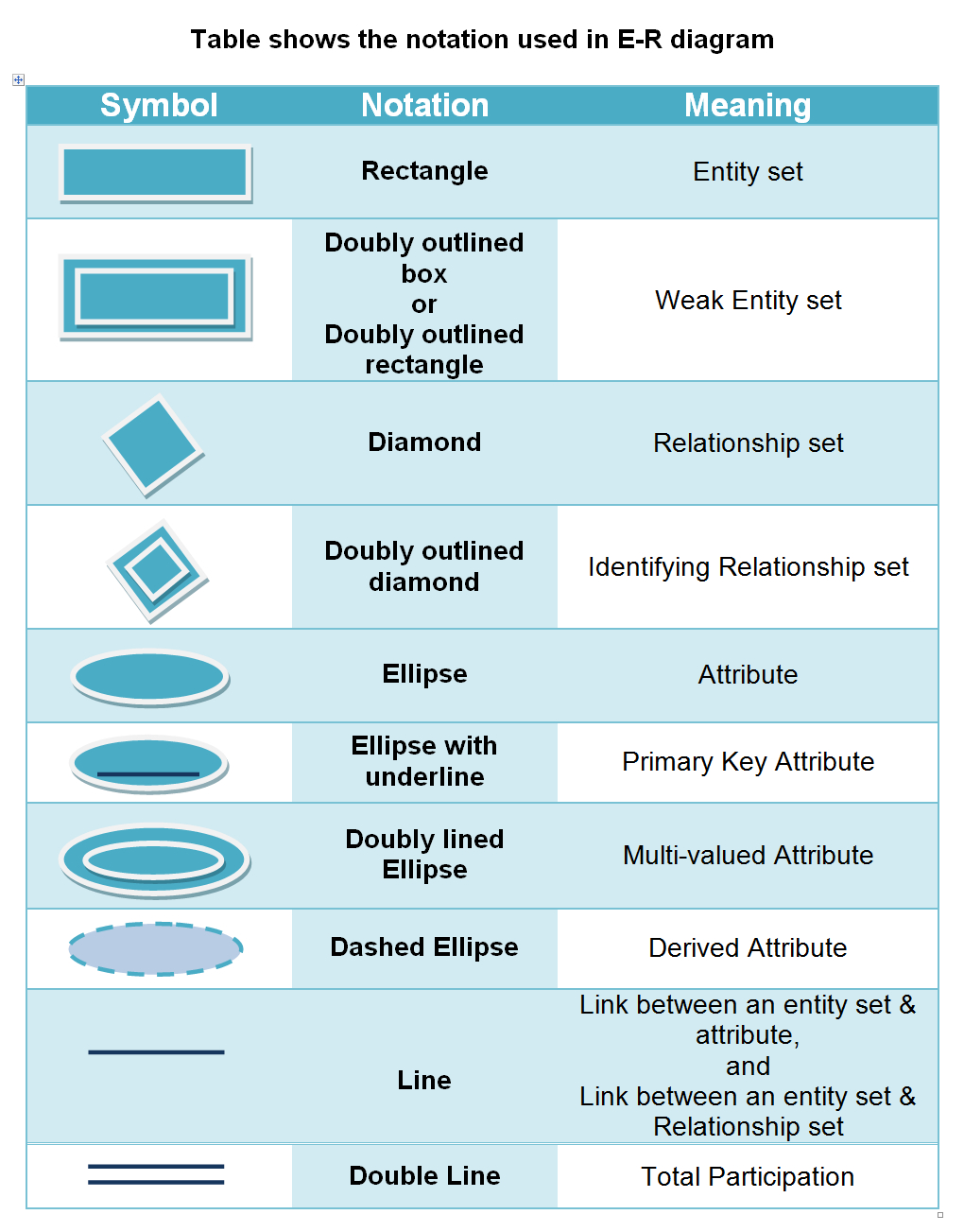
4. E-R (Entity Relationship) diagram
The Entity Relationship (ER) Data Model is a detailed logical representation of the entities, associations, and data elements for a system. A graphical representation of the ER data model is known as ER Diagram. An entity is a person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about which the organization wishes to maintain data. An entity has its own identity and attributes that distinguish it from other entities. Different entities have different relationships with one another.
The basic symbols used in ER diagram are:
1.1.4 Concept of Normalization:-
The process of breaking complex relationships into simple relations is called normalization. It reduces redundancy using the principle of non-lose decomposition. Non-loss decomposition is the reduction of a table to smaller tables without loss of information.
Normalization is needed because it represents a database in its normal form to avoid undesirable things.
· Objectives or importance of Normalization are
a) It reduces redundancy.
b) It improves faster storing and indexing.
c) It simplifies the structure of the database.
d) Dependence between the data is identified.
e) Protects from unauthorized users and secures the data in the database.
f) Removes anomalies for database activities.
g) The database model is made more flexible and easier to maintain.
1.1.5 Types of normalization 1 NF, 2 NF, 3 NF
1. First Normal form (1 NF): - For a form or table to become 1 NF all attributes must be atomic. That is, there can exist no repeating groups in an attribute. In every tuple of the relation, each attribute must have a value.
Member
Mem_code | Mem_Name | Class | Book | |||
|
|
| Code | Name | Issue-date | Due-date |
M001 | SUSHMITA
SHRESTHA | 11 | B0012 | Computer | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M002 | SUZAL
GURUNG | 12 | B0014 | Link Eng | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M003 | THIR
PRASAD DAHAL | 12 | B0015 | Math | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M004 | TRILOK
LAMA BAMJAN | 11 | B0034 | Physics | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M005 | YUNIK TAMANG | 11 | B0032 | Chemistry | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
Unorganized Relation
Mem_code | Mem_Name | Class | B_Code | B_Name | Issue-date | Due-date |
M001 | SUSHMITA
SHRESTHA | 11 | B0012 | Computer | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M002 | SUZAL
GURUNG | 12 | B0014 | Link Eng | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M003 | THIR
PRASAD DAHAL | 12 | B0015 | Math | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M004 | TRILOK
LAMA BAMJAN | 11 | B0034 | Physics | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M005 | YUNIK
TAMANG | 11 | B0032 | Chemistry | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
Figure:-Normalization in 1 NF
Problem in 1 NF: -
a) Insert:-In the relation, we cannot enter the details of a member unless he/she has taken a book from the library, i.e. can’t enter information without book information.
b) Delete: - if we want to delete the details of the book, we shall have to delete the member’s detail also.
c) Update:-If a member has taken 5 books from the library, then the member’s details are repeated 5 times in the relation (table).
2. Second Normal Form
(2 NF):- A relation is in 2 NF if it is in 1 NF and each attribute is fully functionally dependent on the primary key.
The problem in 2 NF: -
a) Insert: - We can insert the details of members even if book information is not available.
b) Delete: - We can delete book information without deleting the member’s details.
c) Update: - We can easily insert or delete member information without redundancy.
Member
Mem_codes | Mem_Name | Class |
M001 | SUSHMITA
SHRESTHA | 11 |
M002 | SUZAL
GURUNG | 12 |
M003 | THIR
PRASAD DAHAL | 12 |
M004 | TRILOK
LAMA BAMJAN | 11 |
M005 | YUNIK
TAMANG | 11 |
Book
Mem_codes | B_Code | B_Name | Issue-date | Due-date |
M001 | B0012 | Computer | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M002 | B0014 | Link Eng | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M003 | B0015 | Math | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M004 | B0034 | Physics | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M005 | B0032 | Chemistry | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
Figure:-Normalization in 2 NF
3.
Third Normal Form (3 NF):-
A relation is in 3 NF if it is 2 NF and each non-key attribute is fully functionally dependent on the entire primary key, and not on any other key. That is, no transitive dependencies exist among the attributes.
The 3 NF overcomes all the problems of 2 NF.
Member
Mem_codes | Mem_Name | Class |
M001 | SUSHMITA
SHRESTHA | 11 |
M002 | SUZAL
GURUNG | 12 |
M003 | THIR
PRASAD DAHAL | 12 |
M004 | TRILOK
LAMA BAMJAN | 11 |
M005 | YUNIK
TAMANG | 11 |
Book
B_Code | B_Name |
B0012 | Computer |
B0014 | Link Eng |
B0015 | Math |
B0034 | Physics |
B0032 | Chemistry |
Issue
Mem_codes | B_Code | Issue-date | Due-date |
M001 | B0012 | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M002 | B0014 | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M003 | B0015 | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M004 | B0034 | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
M005 | B0032 | 2075/05/06 | 2075/05/26 |
Figure:-Normalization in 3 NF
1.1.6 Structured Query Language (SQL):-
· It is a standard relational database language.
· It was developed at IBM’s San Jose Research laboratory.
· It is a non-procedure language in that the users specify what must be done, but not how it is to be done.
· There are four basic operations in SQL:
SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT and DELETE.
· The UPDATE statement enables users to update the data, the INSERT statement enables users to insert new data, and the DELETE statement enables users to delete existing data respectively.
1.1.7 Centralized Vs Distributed Database
Centralized database: - The host computer is used to run the DBMS, the application that accesses the database, and the communication facilities that send and receive data from the user’s terminals. The users access the database through either locally connected or dial-up terminals. The terminals are generally dumb.
Advantages of the Centralized Database:-
· Control: -
The Database is easily controlled by higher authorities.
· High security: -
The Database is centralized so there is no chance of data modifications.
· Maintenance: -
The Database is maintained easily because it is centrally stored.
· Speed:-
Working speed is more than the distributed database.
· Cost:-
The database and device required cost is low.
·
Manpower: - Requires less manpower to operate the database.
Distributed Database: - This is a complex type of database
system in which a collection of multiple logically interrelated databases are distributed countries-wide or out of geographical boundaries. The computers in distributed systems communicate with each other through various communication media, such as high-speed networks or telephone lines. These computers do not
share main memory or disc.
Advantages of Distributed Database:-
· Transparency
· Reliability and availability
· Improved performance
· Easier expansion
· Sharing
· Efficient and flexible
· Capacity and increment growth.
1.1.8 Data Security
The protection of data is called data security. It means preventing the loss of data, misuse, disclosure, or unwanted modification of data.
Various methods can be taken to ensure security. Here are some common methods:-
a) Data may be lost due to infection of virus or due to any accident. So to prevent such problems, use backup copies of data.
b) Use of strong passwords to prevent unauthorized use of computers or unauthorized access to online files.
c) Physical prevention, restricting of personal, keeping data under lock and key.
d) Constant checks of security.
e) Use of the latest operating system.
f) Use of excellent antivirus software.
# Data integrity: - Data integrity refers to the validity of data contained in the database. Database integrity can be reduced in many ways including input typing errors, hardware malfunctions, and data transmission errors. To avoid data integrity errors, database programs should use a data validation process, which defines acceptable ranges for each field in the record. If a user tries to input data out of this range, an error message is displayed.
·
Types of data integrity:-
The two integrity rules are called entity integrity and referential integrity.
1. Entity integrity:-Entity integrity is the rule that no column that is part of the primary key may accept null values.
Entity integrity guarantees that each record will indeed have its own identity. In other words, entity integrity prevents the primary key from accepting null values and ensures that one record can be distinguished from the other.
2. Referential integrity:- The Referential integrity rule states that if table A contains a foreign key that matches the primary key of
table B, then values of this foreign key either must match the value of the primary key for some row in table B or must be null.
#DBA (Database Administration):-
An information specialist who has responsibility for the database is called a Database Administration (DMA). Ideally, DBA is a mature
individual with years of computer experience, a wide diversity of technical abilities, and superior managerial skills.
Ø The duties fall into four major areas:
- Database planning, implementation, operation, and security.
Typical responsibilities of a DBA are:-
1) Helps an organization to decide which department will be responsible for the maintenance and update of each data field in a database.
2) Assures access to database information to each department that needs it.
3) Secures databases from authorized use.
4) Protects databases from physical harm.
5) Co-ordinates the work of individuals making file making file modifications, policy changes, and improvements to the database.
Some of the advantages of the database system in comparison to a manual system are:-
1) Redundancies and inconsistencies can be reduced.
2) Better services to the users.
3) Flexibility of the data system is improved.
4) Cost of developing and maintaining the system is lower.
5) Data integrity, security, etc can be improved.
Ø Data Dictionary:
A data dictionary is a file that contains metadata that is data about data. It is also called an information system catalog. It keeps all the information about the database system such as location, size of the database, tables, records, fields, user information, privileges, backup system, recovery system, etc. It also defines the data types for each
field etc. A good data dictionary always ensures the consistency in database.
Ø Data Manipulation Language (DML):
A data manipulation language (DML) is the language that enables users to access data as organized by the appropriate data model, i.e. DML is used to update the database by adding new data or modifying or deleting the existing data.
Example:
To insert data to the table “record” which contains data like name, address, telephone
insert into record values(“PLK”, “Kathmandu”, 94128);
Ø Data Definition Language(DDL):
A database scheme is specified by a set
of definitions expressed by a special language called a DDL. The logical
structure and files within the database may be defined using DDL. Attributes such as record layouts, fields, and key validation can be described using a DDL.
Example: A table “record” which contains fields like name, address, and telephone can be created with DDL.
Create table record (Name varchar(50),
Address varchar(50),
telephone int);